The Western Australian Department of Health has a statutory responsibility to protect the government and the general community from unnecessary costs and losses. This includes the human cost of adverse incidents. Clinical risk management is also part of a good clinical governance system through which organisations are accountable for continuously improving the quality of their services and safeguarding high standards of care.
In complying with its statutory responsibility, other public sector governance requirements and relevant Policy Frameworks (Clinical Governance, Safety & Quality Policy Framework and Risk, Compliance & Audit Policy Framework), the Department of Health requires all health service providers to focus on local implementation and review of clinical risk management systems.
All staff have a responsibility to understand and employ risk management in their day-to-day work to provide a safe and secure environment for patients, carers and staff. This should be an environment where there is transparent responsibility and accountability for identifying and managing risks, issues and opportunities so that excellence in clinical care may flourish.
Clinical risk management process
The systematic risk management process as outlined in the Australian/New Zealand Standard AS/NZS ISO 31000:2018 Risk Management (PDF 267KB) (external site) should be used in clinical risk management practice. The process involves five steps and two overarching processes as shown in the diagram below.
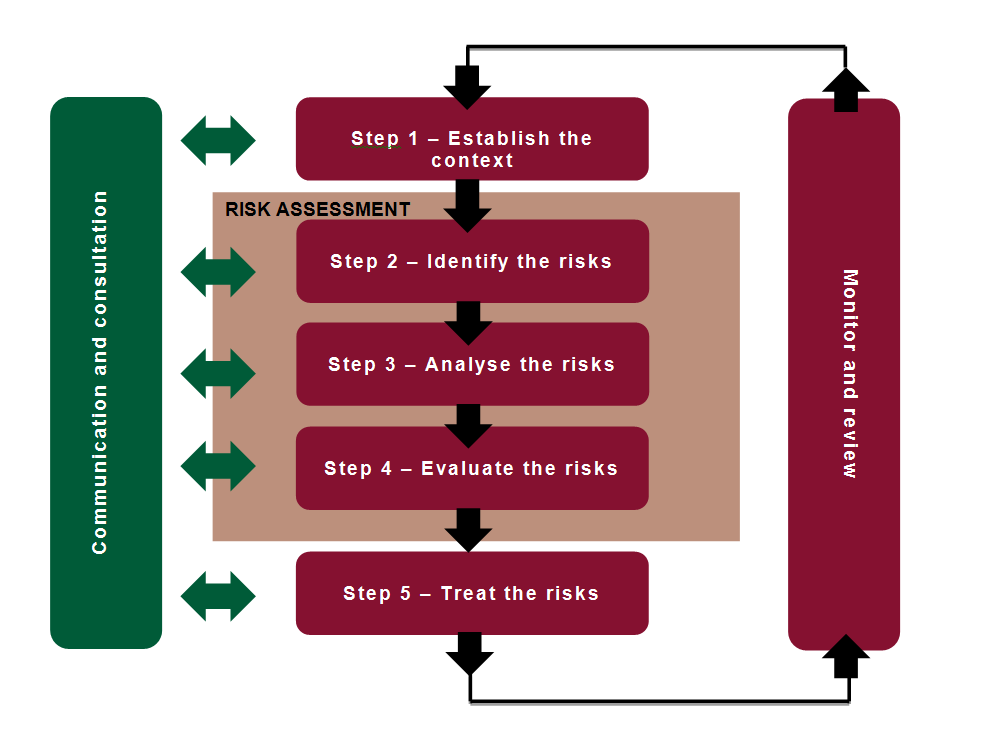
Read more about the process in the Clinical Risk Management Guidelines (PDF 721KB) which include examples to illustrate how to apply risk management in a clinical setting.
A key part of the clinical risk management process is to establish, implement and review controls to address risks. Controls are policies, processes, checklists, actions and safeguards that are actually in place to address risks. Appendix D in the Clinical Risk Management Guidelines highlights examples of WA Health clinical controls against a range of clinical areas.
Resources
More information
Patient Safety and Surveillance Unit
Email: pssu@health.wa.gov.au
Last reviewed: 08-04-2022
Produced by
Patient Safety Surveillance Unit